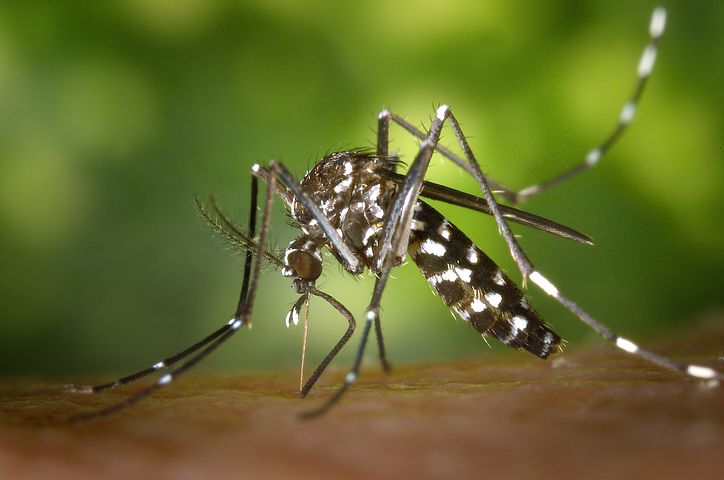
One of the more common deadly diseases of dogs is heartworm disease, which can be prevented. Heartworm disease can occur in cats with about the frequency of winning the lottery.
The adult worms, which may be three inches long, live inside the dog’s heart. They will cause heart disease, but also they’ll drift into the lungs, where they will cause respiratory disorders. The adult worms produce microscopic larvae (babies) called microfilaria. These circulate in the dog’s bloodstream and can also cause organ damage.
The disease is transmitted by mosquitoes. If a mosquito bites a microfilaria-positive dog, it will ingest some of these microfilaria along with a blood meal. When the mosquito bites the next dog, it injects some of these infective larvae into the dog’s blood stream. They will migrate to the heart and grow into adult heartworms, and the cycle begins again.
Heartworm disease is a treatable disease, however the treatment carries risks, mostly due to the tissue damage and organ damage already present in the dog. Delayed treatment may result in heart failure and/or permanent damage to the liver, lungs, and kidneys – possibly causing eventual death.
Currently, some veterinarians and vet clinics will simply allow a dog to continue to have a heartworm infection and just give heartworm prevention. The strategy is to save money. That’s it.
The heartworm prevention that is given stops the heartworms from reproducing and the adult heartworms die of “old age” within 2 years. Meanwhile, the heart and lungs are damaged by the heartworms.
Unfortunately, the signs of heartworm disease, such as coughing, lethargy, and weight loss occur after the disease process is well underway, perhaps as many as three years after the dog becomes infected. In my practice, animals are symptomatic in 2 years or slightly less. Annual heartworm testing is important to detect a problem before permanent damage or death occurs.
It is therefore important to have your dog’s blood tested yearly. The earlier this disease is detected, the greater the chances are of your dog surviving the treatment. Also, some infected dogs will have reactions if given a preventative while carrying the disease, which can be fatal, and this would be prevented by checking for the presence of adult worms. There are two basic preventive programs provided by our clinic. Your choice between the two types depends on what program is more practical and convenient for you.
- Monthly chewable (preferred)
- Monthly topical
Our office does not recommend or endorse Revolution, or any of the cheap knock-off heartworm preventatives being made available these days. There are two now, that are supposed to give me “wider profit margins” (Iver-Hart) to quote the drug-representative, however I do not trust the products. Nor do they present ANY warranty of fitness.
In the southeastern United States, I recommend that medication be given all year long since our mosquito season is variable. Also, stopping in the Fall permits maturation of the last mosquito’s microfilarial inoculation.
Basic Facts on Heartworm Disease
1. It’s treatable
2. It’s preventable
3. It’s carried by Mosquitoes
4. Costs less than 125$ per year to prevent (Depends on the size of your dog)
5. Costs over 600$ to treat
6. Usually fatal within 3 years of contraction.
Starting the preventative before the pups are 6 months old saves you the expense of a heartworm test before starting the preventative. Then a test each year will ensure that no adults are surviving the medication.