Page 100 - Raw Diet References Book 2019
P. 100
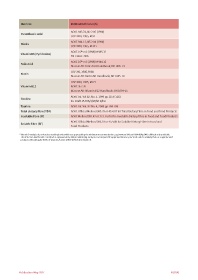
Nutrient Method Reference(S)
AOAC 945.74 /42.2.05 (1990)
Pantothenic Acid
USP XXIII, 1995, M 91
AOAC 944.13 /45.2.04 (1990)
Niacin
USP XXIII, 1995, M 441
AOAC 16th ed. (1998) M 985.32
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
EN 14663: 2005
AOAC 16th ed. (1998) M 944.12
Folic Acid
Biacore AB: Folic Acid Handbook; BR 1005-19
USP XXI, 1986, M 88
Biotin
Biacore AB: Biotin Kit Handbook; BR 1005-18
USP XXIII, 1995, M171
Vitamin B12 AOAC 952.20
Biacore AB: Vitamin B12 Handbook; BR 1004-15
AOAC Int. Vol 82, No. 5, 1999 pp 1156-1162
Choline
EG-Draft 15.706/1/VI/68-D/bn
Taurine AOAC Int. Vol. 82 No. 4, 2000 pp 784-788
Total dietary fibre (TDF) AOAC Official Method 985.29 or 45.4.07 for Total Dietary Fibre in Food and Food Products
Insoluble fibre (IF) AOAC Method 991.42 or 32.1.16 for the Insoluble Dietary Fibre in Food and Food Products
AOAC Official Method 993.19 or 45.4.08 for Soluble Dietary Fibre in Food and
Soluble fibre (SF)
Food Products
* Vitamin D analysis of pet foods containing levels which are approaching the minimum recommendation, say between 500 and 1000 IU/kg DM is difficult and unreliable.
The detection limit for HPLC methods is approximately 3000 to 5000 IU/kg. Analysis is not required if supplementation is practised and it is unlikely that un-supplemented
products with adequate levels of vitamins A and E will be deficient in vitamin D.
Publication May 2017 40/100